Summary
Kafka consumer로 Topic의 메시지를 가져와서 해당 메시지들을 Hbase로 적재를 할 수 있다. Hbase server와 client 간은 thrift 통신을 하는데,
Python에서는 Happybase라는 패키지를 이용하여 thrift 통신을 할 수 있다. Kafka와 Hbase가 이미 설치 되어 있는 상태로 진행하였다.
| Port | Desiption |
|---|---|
| 9092 | Kafka port |
| 9090 | Hbase server와 client 간의 thrift 통신을 위한 port |
Kafka Producer 생성 및 Kafka consumer console로 메시지 읽기 확인
- Producer
class Producer(threading.Thread): def __init__(self): threading.Thread.__init__(self) self.stop_event = threading.Event() def stop(self): self.stop_event.set() def run(self): producer = KafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers='localhost:9092') while not self.stop_event.is_set(): producer.send('my-topic1', b"<<<<<<<<< my-topic test") producer.send('my-topic1', b">>>>>>>>>> test") time.sleep(1) producer.close() - Server Kafka Consumer
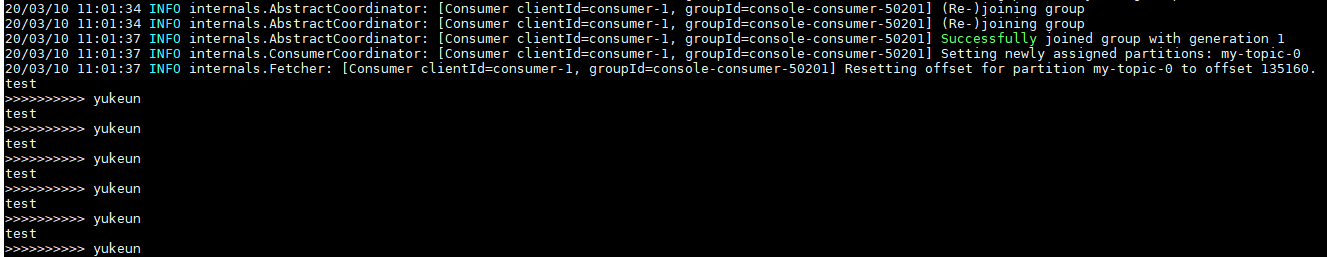
Kafka consumer로 Topic의 메시지를 읽을 수 있는 지 확인
- Local Consumer(PyCharm)
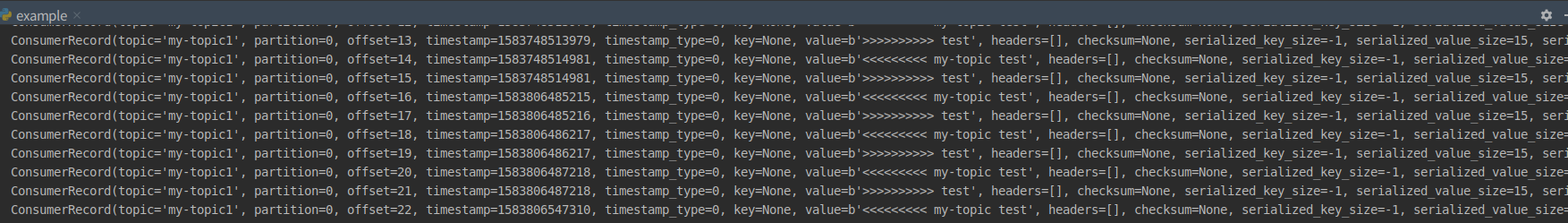
Hbase client 로 Hbase Tables CRD 되는지 확인
- Local(PyCharm console)
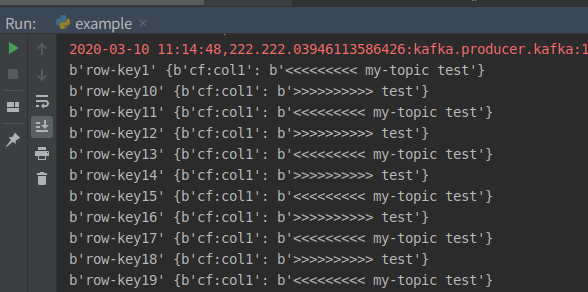
- Hbase shell
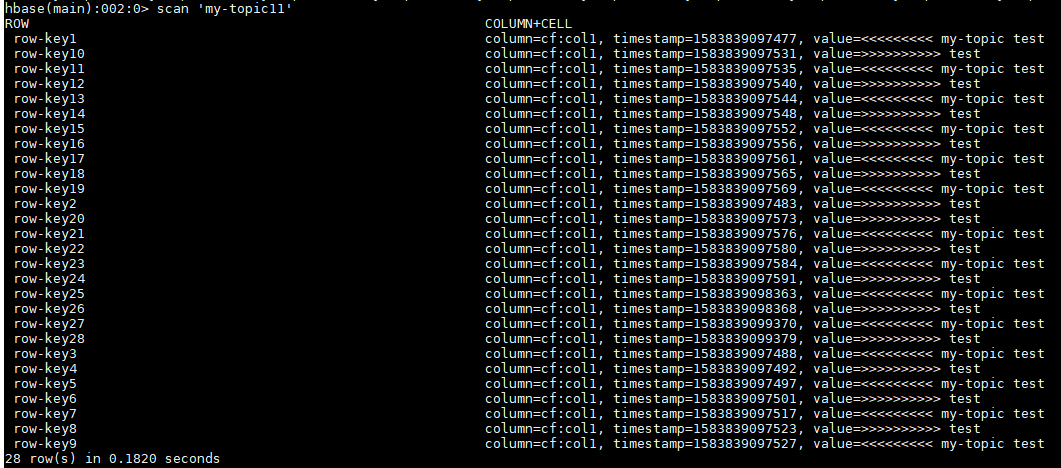
Consumer를 통해 topic을 읽고 해당 메시지들을 Hbase에 적재
class Consumer(multiprocessing.Process):
def __init__(self):
multiprocessing.Process.__init__(self)
self.stop_event = multiprocessing.Event()
def stop(self):
self.stop_event.set()
def run(self):
consumer = KafkaConsumer(bootstrap_servers='localhost:9092',
auto_offset_reset='earliest',
consumer_timeout_ms=1000)
consumer.subscribe(['my-topic1'])
connection = happybase.Connection(host='localhost', port=9090)
connection.open()
table = connection.table('my-topic11')
count = 0
while not self.stop_event.is_set():
for message in consumer:
count += 1
table.put('row-key' + str(count), {'cf:col1': message.value})
if self.stop_event.is_set():
break
for key, data in table.scan():
print(key, data)
consumer.close()
Etc…
Web을 통하여 해당 데이터를 확인하기 위해서는 Ozzie나 Hue 등을 사용 해야 쉽게 데이터를 확인 가능하다.
해당 소스는 Git 레파지토리에서 확인 가능하다.